TCAR May Have Potential For Reducing Carotid Artery Readmissions
In Heart Failure
Get Dexur’s Personalized Hospital Specific Presentation on Quality, Safety, Compliance & Education
By: James Pitt Aug. 16, 2018
When plaque builds up in the arteries that carry blood to the brain, the patient has carotid artery disease. This disease creates a great risk of stroke, because plaque can break off and cause an obstruction in vessels in the brain. Carotid artery disease is involved in 8% of ischemic strokes. Per Weber and Clair 2014, “Carotid artery disease leading to stroke is one of the primary causes of serious long-term disability in the United States today.”
Common treatments are carotid artery stenting (CAS) and endarterectomy (CEA). A 2017 review concluded that CAS was associated with higher risk of stroke or death than CEA. However, a novel variation on CAS, called transcarotid artery revascularization (TCAR), shows promise. Two June 2018 retrospective studies published in Journal of Vascular Surgery presented evidence that TCAR is safer.
The first of these June 2018 analyses found that TCAR was safer than the traditional transfemoral approach to CAS. “Patients undergoing TCAR had significantly more medical comorbidities but similar stroke/death rates and half the risk of in-hospital TIA/stroke/death. These results persisted despite rigorous adjustment and matching of potential confounders.”
The second analysis found found lower 30-day mortality and stroke rates in patients who received TCAR than in matched controls who received CEA. The authors highlight that the TCAR population had higher risk factors (diabetes, coronary artery disease, and tobacco use) than the matched CEA controls. However, the TCAR population also received more pharmaceutical intervention, particularly postoperative clopidogrel. The ongoing CREST-2 trial and VQI-TCAR registry will produce more definitive comparisons of TCAR to CEA.
To examine the burden of 30-day adverse events in CAS, Dexur analysts examined all-cause 30-day readmissions at hospitals in Texas.
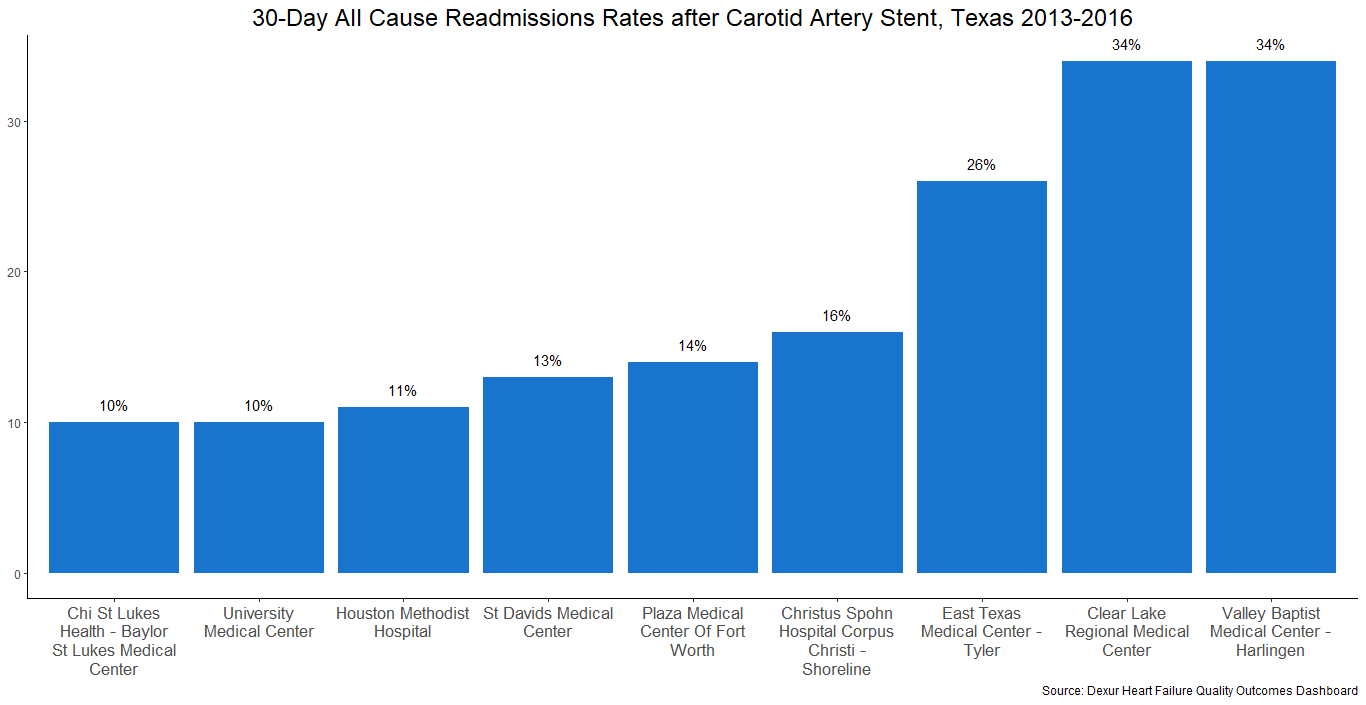
The highest readmission rate was 34%, a tie between Clear Lake Regional Medical Center (Webster, TX) and Valley Baptist Medical Center (Harlingen, TX). The lowest rate was 10% at CHI St. Luke's Health (Houston, TX).
DEXUR PRO MEMBERS GET ACCESS TO:
- Total Discharges ( Jan 2013 to Dec 2016 )
- Total Discharges After Exclusion
- All Cause 30 Day Readmissions
- State 30 Day Heart Failure-specific Readmission Rate
- National 30 Day Heart Failure-specific Readmission Rate
- State 30 to 60 Day Heart Failure-specific Readmission Rate
- National 30 to 60 Day Heart Failure-specific Readmission Rate
For carotid artery stent procedures (diagnosis-related groups 34, 35, and 36) at the following hospitals from 2013-2016:
- University Medical Center (Lubbock, TX)
- Christus Spohn Hospital Corpus Christi - Shoreline (Corpus Christi, TX)
- Plaza Medical Center of Fort Worth (Fort Worth, TX)
- Clear Lake Regional Medical Center (Webster, TX)
- St Davids Medical Center (Austin, TX)
- CHI St Lukes Health - Baylor St Lukes Medical Center (Houston, TX)
- Valley Baptist Medical Center - Harlingen (Harlingen, TX)
- East Texas Medical Center - Tyler (Tyler, TX)
- Houston Methodist Hospital (Houston, TX)
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
