Vital Patch Can be Evaluated by Hospitals By Monitoring Readmissions for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation in DRG 308
In Atrial fibrillation (AFib)
Get Dexur’s Personalized Hospital Specific Presentation on Quality, Safety, Compliance & Education
By: Gokul Menon Nov. 27, 2020
Cardiac arrhythmias are conditions that cause irregular heart rates. Studies say that it is quite a common condition that can go unnoticed because of its asymptomatic nature. Thus, accurate diagnosis plays a key role in reducing mortality. ECG (Electrocardiographic) monitoring is one of the most common methods used to detect arrhythmias. With the advent of technological advancements, monitoring of vitals using wireless devices has taken precedence over traditional methods. These advanced biosensors possess the ability to predict major events like arrhythmias before they occur. These biosensors continue to reshape patient-physician relationships by opening up the possibility of continuous ECG monitoring even in an outpatient setting.
Patch devices contain detection algorithms that help in distinguishing Atrial Fibrillation (AF) from other arrhythmias. This study also goes on to show that a 24-hour ECG monitoring was highly ineffective in detecting AF, compared to “72-hour or 21-day monitoring” among patients with acute ischemic stroke. It further stresses on the sheer increase in diagnostic yield through wireless patch devices, when compared to traditional ECG monitoring. A Study comparing the ECG patch with a 24-hour Holter monitoring system found that the patch allowed continuous monitoring, resulting in improved detection of paroxysmal arrhythmias. Wireless devices such as a patch, helps both physicians and patients in multiple ways. These devices go a long way in improving the efficiency of disease management. They also help in reducing readmission rates and unnecessary visits to the clinic. Remote monitoring of vitals goes a long way in reducing both time and cost.
Vital Patch is one such wearable “on-body” cardiac monitoring device that, when integrated with a patient monitoring device, can assist in saving lives through early detection. This Bio-sensor monitors eight physiological measurements continuously, in real time. In addition to being wireless, this device is also water-resistant and weighs only eleven grams. The VitalPatch device can perform detection of ventricular ectopic beats, pause, atrial fibrillation or flutter, sinus rhythms, second degree AV block, supraventricular tachycardia, idioventricular rhythm, ventricular bigeminy, and ventricular trigeminy, and measurement of heart rate. Vital Patch is the next step in design and development in terms of cardiac monitoring devices. It can monitor the vitals of a patient even after their discharge from the hospital. Post-discharge and Remote monitoring of the patient’s vitals goes a long way in improving recovery time and reducing the rate of readmission. The device makes use of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS). This assists in reducing risk among patients through intelligent and early monitoring. The device can provide hospital-level monitoring at home and quality care of this kind can help reduce readmission.
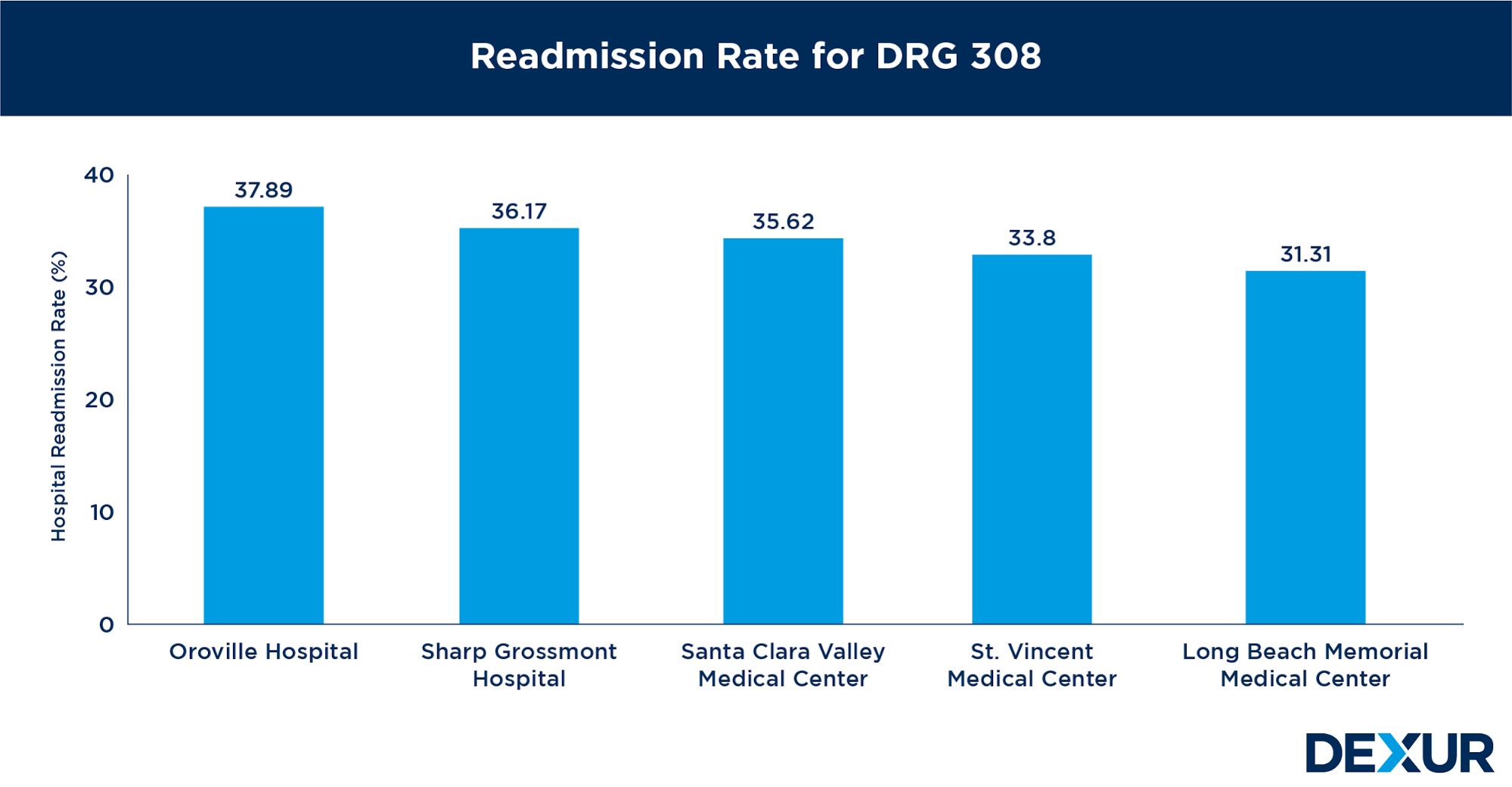
To understand the need for advanced cardiac monitoring, Dexur analyzed Medicare Claims data (April 2017- March 2020) on patients with Arrhythmia who have major complications or comorbidities (DRG 308) and Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (DRG 308 with I480) in five major hospitals in California. In terms of readmission for patients with Arrhythmia in California, Oroville Hospital has the highest rate of readmission with 37.89%. Sharp Grossmont Hospital is a close second with 36.17 %.

Among the five major hospitals with high readmission rates for DRG 308 with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation, St. Vincent Medical Center has the highest readmission rate with 41.17%. Santa Clara Valley Medical Center and Oroville Hospital are a close second and third with 38.89% and 36.84%.