Mortality Rates Nearly Double with Hyperkalemia in California DRG 871 Sepsis Patients
In Hyperkalemia
Get Dexur’s Personalized Hospital Specific Presentation on Quality, Safety, Compliance & Education
By: James Pitt Jul. 03, 2018
Hyperkalemia, i.e. high potassium, is a common electrolyte imbalance. Like other forms of fluid imbalance, it may affect sepsis outcomes. Dexur has extensively reported on fluid imbalance in sepsis.
Following up on a previous report on sepsis mortality in California, Dexur analysts examined in-hospital mortality rates among patients with and without sepsis in California. The sample was CMS inpatient discharges from 2013-2016, at selected California hospitals in zip codes starting with 94 or 95, including the Bay Area and coastal Northern California.
15 hospitals reported mortality rates in sepsis with major complications or comorbidities (DRG 871) by hyperkalemia status. At all of these hospitals, mortality with hyperkalemia was much higher than mortality without hyperkalemia.
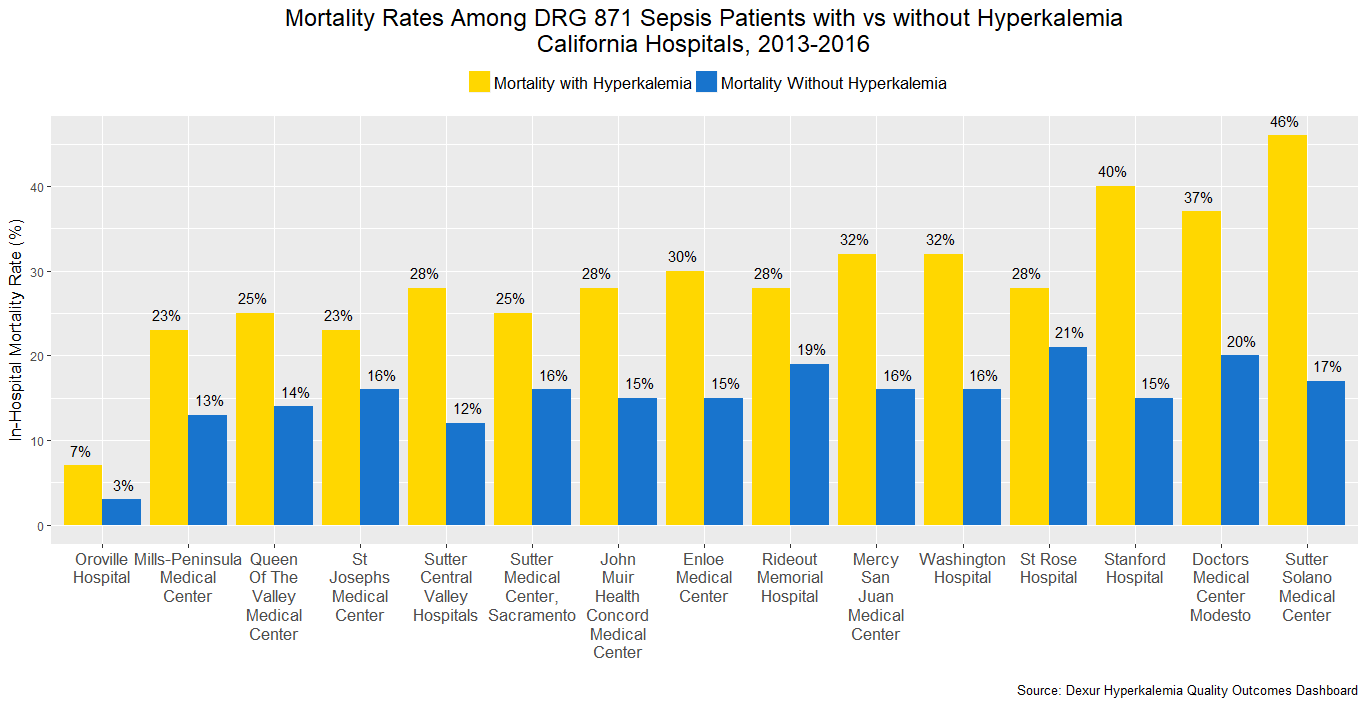
The highest in-hospital mortality rate for DRG 871 patients with hyperkalemia was 46% at Sutter Solano Medical Center (Vallejo, CA). The lowest was 7%, at Oroville Hospital (Oroville, CA).
Hospitals that treated more DRG 871 patients had lower DRG 871 mortality, with or without hyperkalemia. This may indicate familiarity plays a role in these outcomes.
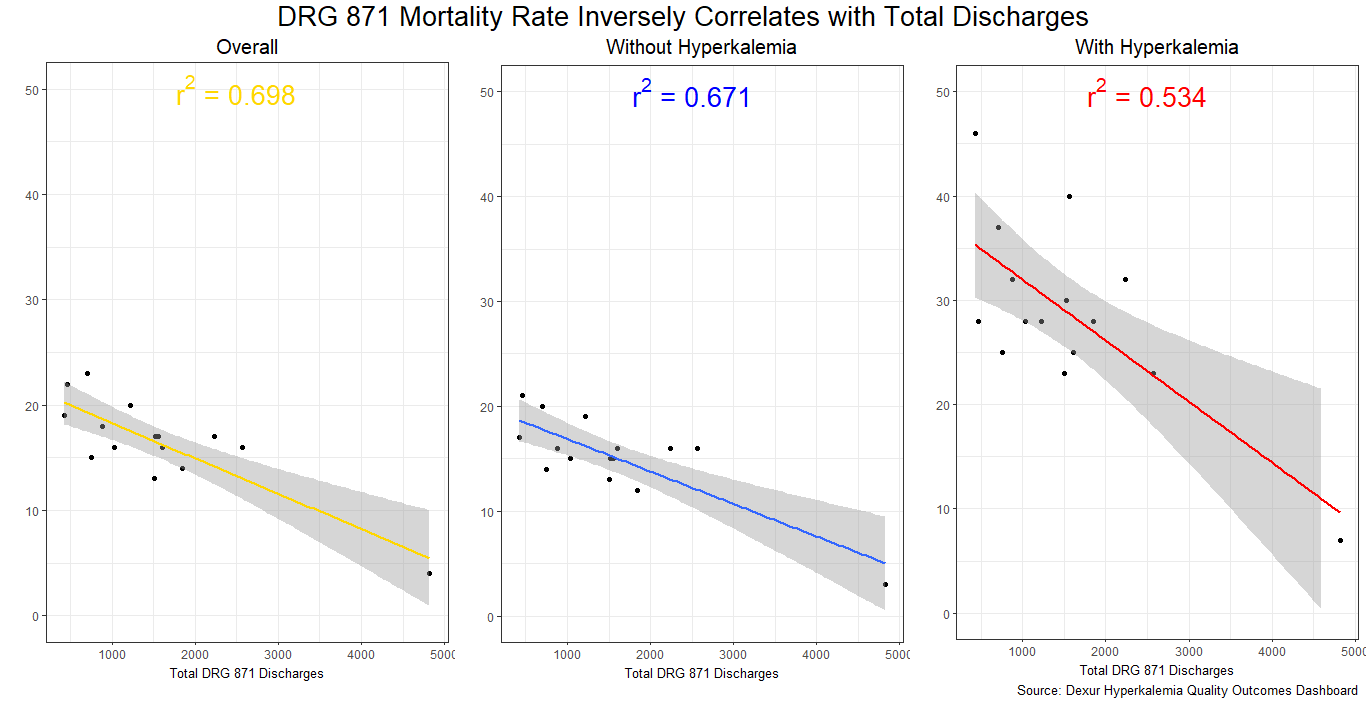
Note that much of the correlation is driven by Oroville Hospital (Oroville, CA), which had an unusually large number of DRG 871 discharges. If Oroville Hospital is not included, the variance in mortality rates explained by total DRG 871 discharges at the remaining hospitals is r^2 = 0.292 for overall DRG 871 mortality, r^2 = 0.206 for mortality without hyperkalemia, and r^2 = 0.162 for mortality with hyperkalemia.
Hyperkalemia is particularly common in patients with renal failure, and pre-existing renal failure is associated with worse sepsis outcomes. Renal failure patients with risk factors for sepsis may need special precautions.
DEXUR PRO MEMBERS GET ACCESS TO:
- Total DRG 871 Discharges
- Total Hyperkalemia Discharges at DRG 871
- % of Hyperkalemia Discharges at DRG 871
- Mortality Rates at DRG 871
- Mortality Rates without Hyperkalemia at DRG 871
- Mortality Rates with Hyperkalemia at DRG 871
- Difference in Mortality Rates with & without Hyperkalemia
- State Difference in Mortality Rates with & without Hyperkalemia
- National Difference in Mortality Rates with & without Hyperkalemia
From 2013-2016, at the following hospitals:
- Stanford Hospital (Stanford, CA)
- Washington Hospital (Fremont, CA)
- John Muir Health Concord Medical Center (Concord, CA)
- Mills-Peninsula Medical Center (Burlingame, CA)
- Queen Of The Valley Medical Center (Napa, CA)
- St Rose Hospital (Hayward, CA)
- Sutter Solano Medical Center (Vallejo, CA)
- Enloe Medical Center (Chico, CA)
- Sutter Medical Center, Sacramento (Sacramento, CA)
- Sutter Central Valley Hospital (Modesto, CA)
- Oroville Hospital (Oroville, CA)
- Mercy San Juan Medical Center (Carmichael, CA)
- St Josephs Medical Center (Stockton, CA)
- Rideout Memorial Hospital (Marysville, CA)
- Doctors Medical Center Modesto (Modesto, CA)
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
